AWS dictionary
| Item | Definition | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| AMI | Amazon Machine Image | It is a pre-configured package required to launch an EC2 instance. It includes the OS, software packages and settings. AMI |
| AWS | Amazon Web Services | |
| CLI | Command Line Interface | A tool to manage AWS services from the command line, suitable for automation tasks and scripts |
| EBS | Elastic Block Storage | A type of virtual hard drive of EC2 instances EBS |
| EC2 | Elastic Compute Cloud | A virtual server in AWS EC2 |
| IAM | Identity and Access Management | Handles the management of policies of users, groups and roles of an AWS account |
| IOPS | Input Output operations Per Second | Amount of data that can be written on or retrieved from an EBS volume per second |
| S3 | Simple Storage Service | AWS service that allows the storage of any type of data in “root” folders called buckets. Inside a bucket there can be folders and objects (files) S3 |
| Snapshot | EBS volume snapshot | Is an image of an EBS that can be stored as a backup or used to create a duplicate. Acts as a template of a new EBS |
| VPC | Virtual Private Cloud |
EC2 instances
EC2 instances can be created with the AWS console (that is, logged in to the AWS account using the web browser). You can manage all the instances created within a specific AWS region. VPC’s are associated to AWS regions, there can be several VPC’s in a given region. Each region has several availability zones (default subnets, i.e., ip ranges). But it is possible to create further subnets within each of the availability zones. It is necessary to perform several steps when creating an EC2 instance, some of these steps have default values:
- Choose the VPC and subnet where the instance will be created
- Choose the AMI type (OS type and version)
- Choose the processor type
- Assign a Security Group to the instance to allow/disable incoming and outgoing traffic
- Attach new or existing EBS volumes. Each instance is created at least with one root volume.
- Use a custom user data script to perform some tasks at startup
- Select an existing ssh key-pair or create a new one
ssh access to EC2 instances
When creating an EC2 instance it is necessary to attach an existing ssh key pair or create a new one.
For Amazon Linux AMIs, this will guarantee that the public ssh key will be added to the .ssh/known_hosts file of the user ec2-user.
The key pairs are manually created in the AWS EC2 console, and it is only possible to obtain the private key file during the creation time.
The private ssh key must be in custody of every host that want to ssh access the EC2 instance, but note that there must be also specific rules in the EC2 instance Security Group allowing ssh traffic through port 22 coming from the IP of the requesting hosts.
AWS CLI
The AWS Command Line Interface must be installed and configured to connect to a specific AWS account. The installation is trivial, but to properly configure the CLI it is necessary to create access credentials to the AWS account. For this, the first step is to login to the AWS account and select the IAM service. The credentials are associated to AWS users, which are further associated to groups.
- Create a group including the necessary policies (related to EC2 services, AdministratorAccess or others)
- Create a user:
- Choose access type (check Programming access for CLI)
- Add the user to a group
- Take note of the public and secret access keys
Example of public and private user access keys are: AKFAQNOK7RH4RAFKTWWJ and GGlxnpdnnQzGAlKm4LThSjQohZ8kP1IRimUdGzfd.
The next step is to run the initial CLI configuration and provide the necessary parameters (keys, AWS region and output format):
$ aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [None]: AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY
Default region name [None]: us-west-2
Default output format [None]: json
AWS Lambda service
AWS Lambda is a service that allows to run code without a server. With wide applications, using Lambda one can trigger code scripts in any supported language (python, java, Node.js…) to perform many tasks such us, for example, performing an automatic resizing of images when uploaded to an AWS S3 bucket.
AWS Lambda function to stop/start of EC2 instances
Let us follow this tutorial to manually configure a Lambda function which will stop and start EC2 instances.
- First we go to the IAM console and create a new policy for the AWS Lambda role, pasting the following code in the JSON editor. Continue and finish the policy creation. Policies are needed by users and roles to perform specific actions on AWS ressources. In this case, any AWS Lambda role with this policy attached will be able to start/stop EC2 instances as well as to perform some actions related with Amazon CloudWatch logs.
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "logs:CreateLogGroup", "logs:CreateLogStream", "logs:PutLogEvents" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:logs:*:*:*" }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "ec2:Start*", "ec2:Stop*" ], "Resource": "*" } ] } -
Next, we create the AWS Lambda role and we attach the policy created above.
- We access to the AWS Lambda console, and we create a new function from scratch:
- We need to provide a name, e.g., startEC2Instance
- Choose a programming language to create the function (python 3.8
- Associate an existing role (the one created in step 2)
- Click on create function and paste this code in the editor (it is python 3 code)
import boto3
region = 'eu-west-3'
instances = ['i-0431586fa6606dcdf']
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2', region_name=region)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
ec2.start_instances(InstanceIds=instances)
print('started your instances: ' + str(instances))
- Under basic settings section, set the Timeout to 10 seconds.
Repeat the same steps for creating another function to stop a specific EC2 instance, and paste the code
import boto3
region = 'eu-west-3'
instances = ['i-0431586fa6606dcdf']
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2', region_name=region)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
ec2.stop_instances(InstanceIds=instances)
print('started your instances: ' + str(instances))
Remember to change the region and instance id to your specific case.
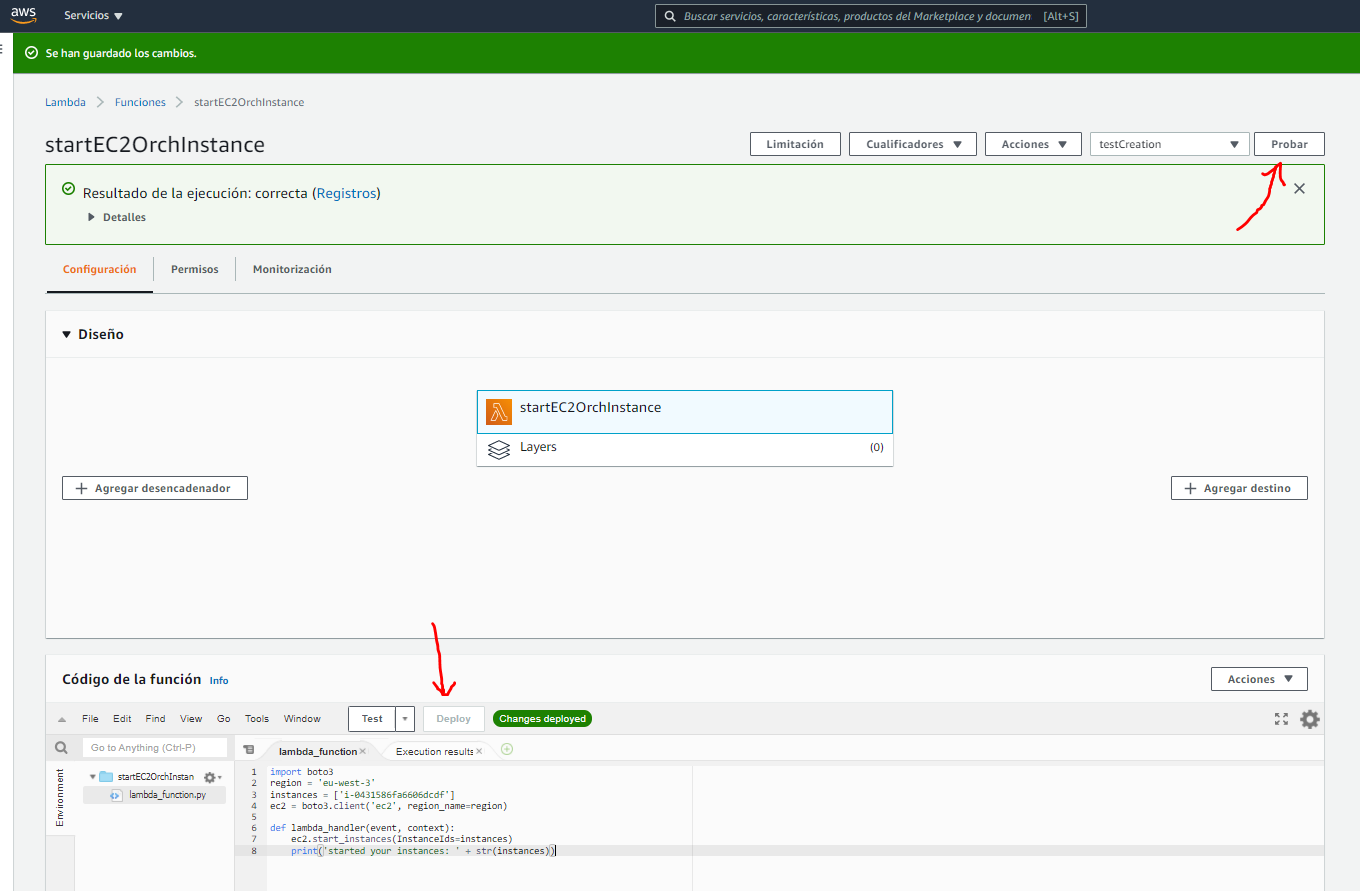
Once the functions are created, it is possible to test them. For this, create a test in each function. Give it a name and click on Create, don’t pay attention to the JSON text box since it is not used to perform the test. Click on test and check if the instance is stopped/started in the EC2 dashboard.
Before running the test, you must save the code changes and click on deploy
Schedule Lambda functions triggering using CloudWatch events
Let us now schedule a safety stop of our instance every day at 19:00 so that we don’t incur in extra charges accidentally.
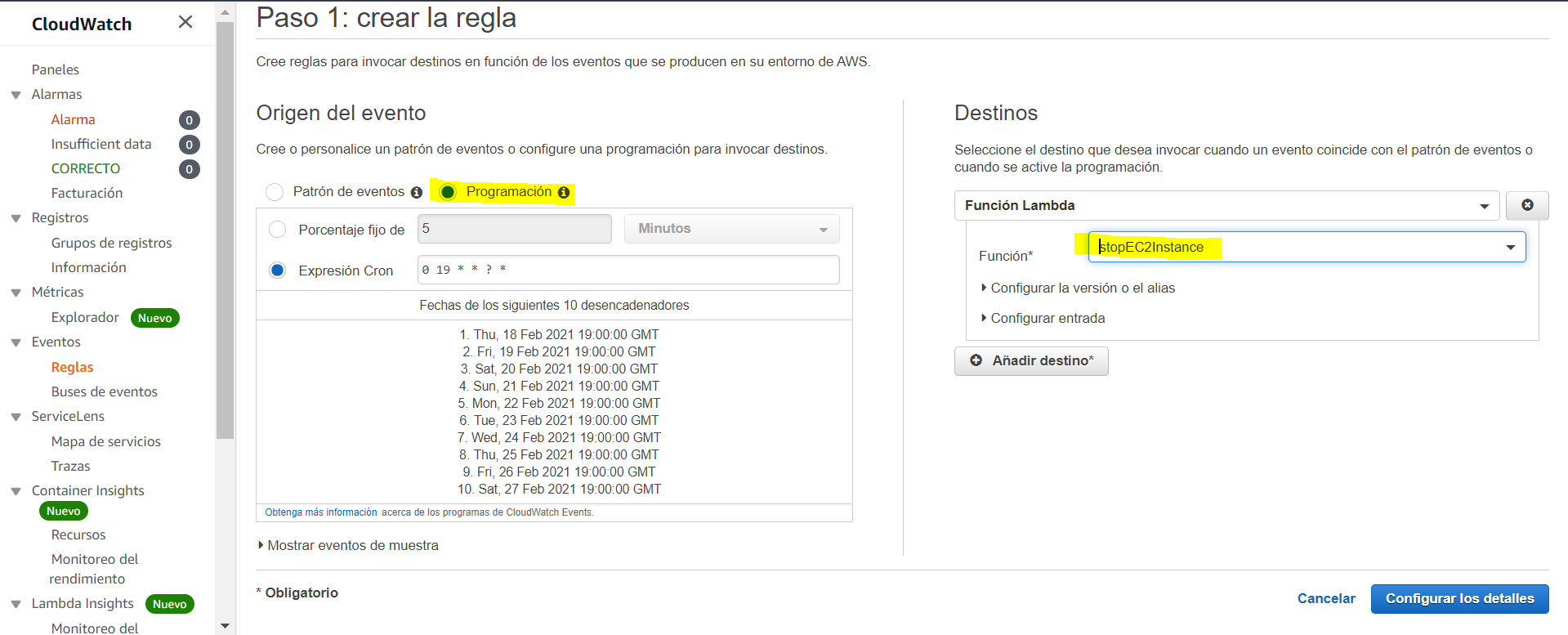
- Navigate to the AWS CloudWatch Management Console
- Choose Rule in the Events section on the left panel
- On the Source of Event section, choose Schedule (Programación in Spanish), and provide the appropriate CRON pattern:
0 19 * * ? *. Checkout the AWS user guide Schedule Expressions for Rules. - On the right panel, in Targets, add the stopEC2Instance Lambda function.
- Finish giving a name and description to the rule.
Return to main page